Business Continuity Planning
- Environmental contamination
- Loss of customers
- Financial loss
- Damage to reputation
- Lawsuits
- Fines and penalties
- Business interruption
- Causalities
- Roles and responsibilities of the Disaster Recovery Teams
- In the event of an emergency, a Disaster recovery call tree with a call tree procedure clarifying the call process.
- Your organization's backup facility details
- Operational considerations if staff must remain in the Standby Facility for an extended time.
- Data and backups
- How communications must be carried out during disasters with authorities, employees, clients, vendors, media, and other stakeholders along with their contact details
- List the tasks that must be completed during the first hour, day, and week of the plan's implementation. Include specifics about when you expect normal business to return, as well as what will signify that your company is ready
- In the event of a disaster, how the disaster will be assessed and prevention strategy of further damage
- Standby facility activation
- Restoring IT functionality
- Repair and rebuilding of primary facility
- Criticality ranking system
- Plan Testing & Maintenance
- Call Tree Testing
XYZ Corporation expected to continue indefinitely; however, they overlooked the importance of business continuity.
They didn't have a framework, instructions, or procedures in place when the weather got awful with huge storms, so they didn't know what to do.

Because they didn't have a list of people to contact, no one was aware that there was a problem. As the storm blasted across town, their IT systems collapsed rapidly.
It was too late for them to realize how fragile was their fireproof when the smoke billowed through the ceiling.
They did all they could to get business back up and running, but the storm struck again in a few months.
Stories like these abound.
In view of the increase in the frequency of accidents, natural disasters, and hacks, how can a business do to cope? A Business Continuity Plan can prevent your company from "falling under" in the event of unforeseen circumstances.

Do you have a business continuity plan prepared to survive if things go off course?
Conducting a Risk Assessment
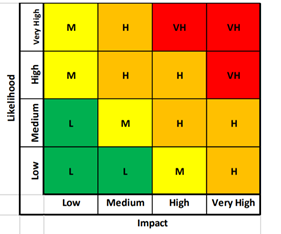
A risk assessment is a method of evaluating potential threats and determining what might happen if they materialize.
Every business confronts its own set of risks. The key to identifying yours is to do a thorough risk assessment. The steps for conducting risk assessments are depicted in the diagram below

What Should be Included in the Business Continuity Plan
1) Business Disruption Scenario Planning
Determine which team members' particular skills/knowledge are required to handle the audit scope efficiently and effectively. Here's where you determine the general qualifications, responsibilities, training and continuing education of the auditors

A solid business continuity plan should include contingency plans for every imaginable scenario, so you and your company are never left defenseless.
Examples of typical things that might create business disruptions include:
Natural disasters: Avalanches, landslides, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions, floods, tsunamis, blizzards, and wildfires may impact supply chains, cause damage to communication infrastructure, buildings, and equipment, cause loss of employees and customers.
Human error: Human errors are unavoidable. You may lose track of key data, delete critical information, or break equipment by accident.
Personal information or data breach: Because the data of your clients must be kept safe and secure, you must have a backup system in place in case it is stolen or lost. Some of the most common workplace disasters are ransomware and cyberattacks, mistakenly deleted files or folders, server/drive crash, and datacenter outage.
Outages of electricity: Power outages are a serious worry that can bring your organization to a pause, whether they're caused by natural disasters or a system breakdown.
2) Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
'A business impact analysis (BIA) is the process of determining the criticality of business activities and associated resource requirements to ensure operational resilience and continuity of operations during and after a business disruption.' - Gartner
By definition, a risk always has a negative impact. The magnitude of the impact, however, differs in terms of cost and influence or another vital aspect.
Consider some of the impacts of risks:
A business impact analysis (BIA) assists you in assessing the impact of each risk and estimating the likelihood of it occurring. It displays which risks necessitate risk mitigation expenditures and effort. Business procedures that are critical to your company's survival are usually at the top of the priority list.
3) Disaster Recovery (DR) Strategy
A disaster recovery (DR) plan must detail how to respond to unforeseen events, and what you can do to resume critical business operations as quickly as possible. Elements of the DR plan include:
It would also be wise to clearly understand for executive management, senior personnel and operational staff to have a firm foundation of the standards of best practice in the critical area Business Continuity and Scenario Planning.
Also, to create a robust business continuity plan, consult extensively within your organization, execute trial runs, update the plan on a regular basis. An effective Business Continuity Software Management Tool can greatly add value to your business.






