Cleanroom Questions Answered
- Airborne particles of viable and non-viable nature
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Air pressure
- Air flow
- Air motion
- Lighting
- Inefficient placement - a design that doesn't support your processes
- Maze-like walkways
- Poor ventilation
- Unable to maintain temperature -too hot, stuffy or freezing cold
- Stakeholder consultations
- Specification of the correct grade
- Power requirements
- Clearance space between the ceiling and walls of your cleanroom and the ceiling and walls of your manufacturing facility for necessary services
- Cold tracking - the movement of temperate along a conductive material
- Interior isolation
- Personnel and workflow
- Static electricity and humidity control
- Capital cost vs running cost
- SOPs to ensure that the cleanroom is effectively operated to maintain air quality
- Authorities and regulatory compliance
- Future expansion
- Cleanroom surface issues
- Rivets presented as a lump of silicon over the top or a hole directly into a stagnant, uncontrolled part of the facility
- Mushroom bolts
- Grey electrical conduit running down the wall
- Windows with a sloping sill
- Completely sealed cleanroom doors
- Bad silicon sealant application
- Insufficient light
- Too much light
- Things that poke into cleanroom environments
- Internally insulated ducting
- Personnel
- Equipment
- Tools - Everyday tools, such as regular household or industrial cleaning products (brooms, mops, dusters) and writing supplies (pen, pencils, paper).
- Raw materials/ Products
- Air in the facility
- The water used in the manufacturing process
- Static electric charge
- Government regulations
- Industry standards
- Customer requirements
- Ease of cleaning
- Restriction of access
- Particulates
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Microorganism
- WHO GMP Guidelines (International)
- WHO Technical Report Series, No. 902, 2002
- Annex 6: Good manufacturing practices for sterile pharmaceutical products
- WHO Technical Report Series, No. 961, 2011
- Annex 5: WHO guidelines on good manufacturing practices for heating, ventilation and air-conditioning systems for non-sterile pharmaceutical dosage forms
- Annex 6: WHO good manufacturing practices for sterile pharmaceutical products
- WHO Technical Report Series, No. 902, 2002
- EEC GMP Guidelines (EU, Partly international)
- US FDA cGMP Guidelines (USA, International)
- ISPE Guidelines (International)
- PDA Technical Report 13 (Revised): "Fundamentals of an Environmental Monitoring Program" (USA)
- DIN EN 12599 (EU, International)
- Volume 4 EU "Guidelines to Good Manufacturing Practice Medicinal Products for Human and Veterinary Use, Annex 1: Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products" (EU).
- PIC/S GMP Guide (Part I: Basic Requirements For Medicinal Products)
- PIC/S Guide To Good Manufacturing Practice For Medicinal Products - Annexes
- USP <1116> "Microbiological Control and Monitoring of Aseptic Processing Environments" (USA)
- 21 CFR (Parts 210, 211, 600-680) - cGMP regulations
- ISO 14698 Standards (3 Parts):
- ISO 14698-1 "Biocontamination: Control General Principles"
- ISO 14698-2 "Biocontamination: Evaluation & Interpretation of Data"
- ISO 14698-3 "Biocontamination: Methodology for Measuring Efficiency of Cleaning Inert Surfaces"
- ISO 14644 Standards (8 Parts):
- ISO 14644-1 "Classification of Air Cleanliness"
- ISO 14644-2 "Clean room Testing for Compliance"
- ISO 14644-3 "Methods for Evaluating &Measuring Clean rooms & Associated Controlled Environment"
- ISO 14644-4 "Clean room Design & Construction"
- ISO 14644-5 "Clean room Operations"
- ISO 14644-6 "Terms, Definitions & Units"
- ISO 14644-7 "Enhanced Clean Devices"
- ISO 14644-8 "Molecular Contamination"
- Ensure that the amount of contamination that escapes from your manufacturing operations is at the minimal level
- Do not provide cleanroom access to anyone who is not trained - People are the largest sources of contamination
- Regularly clean the cleanroom according to strictly controlled procedures
- Regularly maintain all equipment
- Regularly monitor filters and airflows and ensure frequent recertification of the cleanroom
If you are involved in the manufacturing, processing, testing, and release of sterile and non-sterile products, you need to understand the basic concepts of microbiology, microbiological and contamination control practices, cleanroom design, routine testing, qualification/validation, and use of cleanrooms and the sterilization processes within your industry.

ComplianceOnline's seminar 'Cleanroom, Microbiology and Sterility Assurance Practices' provides insights about various key elements of sterility assurance and contamination control such as cleanroom regulations, classification, sources and types of particles, design requirements, validation/qualification, operations, environmental monitoring program requirements, excursion investigations, datatrending, microbiological processes/methodology, and cleanroom cleaning/disinfection.
The following section provides answers to some basic cleanroom questions.
What is a cleanroom?
The FDA defines a cleanroom as an isolated environment, that is strictly controlled with respect to
How is the level of contamination in a cleanroom measured?
A cleanroom has a controlled level of contamination that is specified by the number of particles per cubic meter at specified particle size.
What are the common cleanroom design flaws?
What are the key cleanroom design considerations?
What are some gaps in cleanroom design that could pose a significant risk to the cleanroom's long-term compliance even if the design was not in conflict with the GMP standard or regulation?
What are the sources of cleanroom contamination?
What are cleanroom classifications?
Clean rooms are classified according to the cleanliness level of the air inside them. There are many classification types that govern cleanroom cleanliness, but the key system was laid out by the International Standards Organization. ISO classifications apply to all cleanroom industries and applications. This standard includes the cleanroom classes in this standard include: ISO 1, ISO 2, ISO 3, ISO 4, ISO 5, ISO 6, ISO 7, ISO 8 and ISO 9. ISO 1 is the highest classification according to ISO 14644-1.
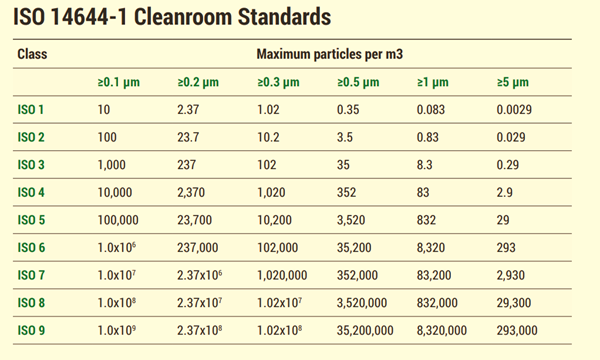
Standards are regulations like USP or ASTM International standards are organized by industry-specific requirements.
What factors determine the level of cleanroom you need?
Different factors determine a cleanroom that meets your needs:
Where to find cleanroom guidelines?
Where to find cleanroom regulations?
What are the ISO Standards for Cleanrooms?
How to maintain a cleanroom?
What are the best practices for handwashing in cleanroom?
Although the use of gloves in a cleanroom is a standard practice, those who wear gloves are less likely to wash or clean their hands before donning them. So, make sure of good hand hygiene to avoid the vulnerability of cleanroom to bacteria or potential introduction or transfer of microbes such as fungus and viruses.






