HOW TO PROTECT YOUR BANK'S TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE AND BUSINESS APPLICATIONS - 9 SIGNIFICANT IT CONTROLS LEADERS MUST BE AWARE OF
How would you want your bank to be known as?
Safe, Secure, Friendly, Trustworthy, Fast, Agile & Simple
Your bank cannot earn a good name on its own. It needs proper IT controls while also maintaining the agility and simplicity. This article will discuss nine essential IT controls senior leaders of banks must be aware of to protect the bank's technology infrastructure and business applications.

The Benefits of IT Control
IT controls are a set of activities performed by a person or a system that has been designed to identify and prevent risks, ensure that the IT operates as intended, the data is reliable and that the organization follows the applicable laws and regulations.
IT controls are usually classified into two categories -
- General controls
- Application controls
Each category and their control areas are shown in the following visual:
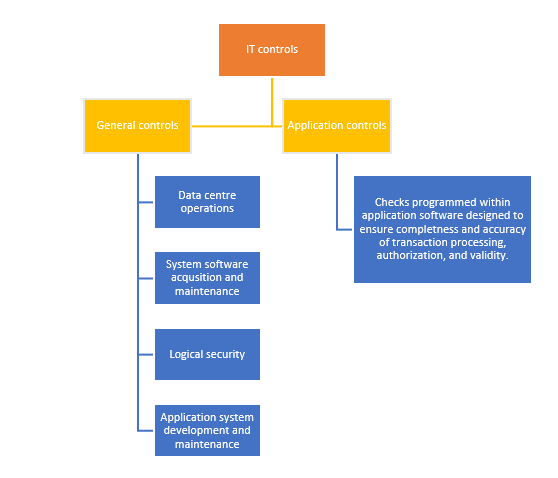
How to identify the right IT Controls for your organization?
- Take help from the guidance provided by the industry governing bodies such as COSO, ISACA, AICPA, FFIEC, OCC, FDIC, Federal Reserve, and others.
- Identify the requirements that are most spoken of, most in news, which is the need of the hour
- Use personal experience
- Listen to customer conversations
- Take clues from prevailing risk factors
- Industry trends, surveys and studies
- Foreseen impact on the organization
9 Significant IT Controls You Must Be Aware of and Have in Place
#1: IT Governance
IT governance implies that IT processes are fully integrated into life-cycle of business process and it influences on quality of service and business agility (Spremic, 2009, pp. 906).
Van Grembergen and De Haes (2005) defined IT Governance as the organizational capacity exercised by the Board, executive management and IT management to control the formulation and implementation of IT strategy and in this way ensure the fusion of business and IT.
Implementing IT Governance ensures that IT delivers value to the bank in an effective way. It provides:
- Strategic alignment: Direction for the strategic alignment of IT with the bank
- Risk management: Determines the IT processes are in place for adequately addressing risks
- Delivers business value: helps IT and the bank to create a partnership designed to drive maximum business value from IT
- IT Performance: Provides the mechanisms to verify strategic IT compliance and performance
- Resource management: Provides direction for sourcing and use of IT resources
#2: Continuous Monitoring and Incident Management
'Continuous monitoring is the process and technology used to detect compliance and risk issues associated with an organization's financial and operational environment.' - Wikipedia
'IT incident management is an area of IT service management (ITSM) wherein the IT team returns a service to normal as quickly as possible after a disruption, in a way that aims to create as little negative impact on the business as possible.' - TechTarget
Continuous monitoring and incident management IT controls involve segregating duties, enlisting key business application risks that can be monitored electronically, Identifying key system settings that require authorization if changes are to be made, Implementing continuous monitoring software or alerts when suspicious or unauthorized activity is performed, ensuring that the antivirus and malware software is up to date, and having a tiered approach to filtering emails.
Continuous monitoring and incident management implementation help in:
- Identifying and preventing the types of attacks and their frequency, the kinds of frauds and the various divisions
- Providing assistance to compliance and audit for more specific analysis
- Developing future strategies for future attacks and containment
#3: Information Security
'Information security, sometimes shortened to infosec, is the practice of protecting information by mitigating information risks. It typically involves preventing or at least reducing the probability of unauthorized/inappropriate access, use, disclosure, disruption, deletion/destruction, corruption, modification, inspection, recording or devaluation, although it may also involve reducing the adverse impacts of incidents.' - Wikipedia
Information security must be viewed as a process. The process involves ensuring that vulnerability and penetration testing including wireless and application are performed periodically, Implementing prevention monitoring/ intrusion detection, monitoring of patches and alerts, ensuring hard drives of laptops, PDA's and external and internal hard drives that store important information is encrypted, ensuring that the fields in applications and fields where sensitive information is presented and stored are encrypted and having a tiered approach to IT security. Performing background checks of employees that have access to customer information are vital as well.
Information security controls implementation and process monitoring aid in achieving integrity, confidentiality, availability, assurance and accountability. It protects the bank from:
- Internal threats such as staff carelessness, internal fraud and theft
- External threats such as hacking, attacks on customers, and cybercriminals
#4: Data Privacy
'Data privacy refers to who's allowed access to consumer information provided to institutions with whom they've entered into a business relationship. Workers at banks need certain information to verify the identities of those accessing an account belonging to a client. Financial advisors require certain client data to enter into a transaction on the behalf of those holding an account with them. Employees in another area may also need this information for other functions within a bank or financial firm.
Problems arise with data security when employees, security officials, and others tasked with protecting sensitive information fail to provide adequate security protocols.' - Angela Springfellow - NGData
Data privacy protection includes activities such as identifying the sensitive information collected/stored the organization, not collecting or storing unnecessary sensitive information, having documented policies for the handling of sensitive information such as collecting, storing, email and reporting, and developing data classification based on sensitivity and business impact. It is important to provide relevant staff training about how to handle sensitive data, and about what is appropriate behavior. It is also critical to have procedures for securely disposing sensitive data, and leverage advanced threat protection solutions.
Few advantages of Data privacy protection are:
- Helps comply with contractual requirements for privacy protections.
- Prevents breaches that hurt businesses and individuals or data subjects
- Helps in maintaining and improving brand value
- Strengthens public, investor and customer trust
#5: Identity and Access Management
'Identity and Access management refers to the processes and methodologies that are used to ensure the right access to right individuals across various information sources of an organization.' - Happiest Minds
Segregation of duties is most important before granting additional access to an account. Identity and access management involves establishing a process to review access rights periodically, implementing role-based security, investing in multiple factor authentication solutions, and having centralized provisioning of users and their access rights.
Business benefits include:
- Easy access from anywhere: customers and partners alike easily and securely access the business capabilities anywhere and at any time.
- Improves employee productivity
- Enhances user experience
- Secures all aspects of the brand
- Increases business agility
#6: Physical Security
Physical security is the protection of personnel, hardware, software, networks and data from physical actions and events that could cause serious loss or damage to an enterprise, agency or institution. This includes protection from fire, flood, natural disasters, burglary, theft, vandalism and terrorism. - Margaret Rouse, Searchsecurity.com
Physical security involves maintaining and accurate inventory of servers and applications, placing servers and network devices in areas that are available only to specifically authorized personnel, restricting administrative access to machines in those limited access areas, ensuring there is no interruption in power supply and that the computers used by vendor and employees for remote access meet security and configuration requirements
#7: Backup and Recovery
Backup is the process of making an extra copy (or multiple copies) of data. You back up data to protect it. You might need to restore backup data if you encounter an accidental deletion, database corruption, or problem with a software upgrade.
Disaster recovery, on the other hand, refers to the plan and processes for quickly reestablishing access to applications, data, and IT resources after an outage.'- IBM cloud education.
A good backup and recovery implementation comprises of defining critical data that is critical to business, storing data at a backup location that is physically different from its original creation and usage location, setting up a backup schedule according to business requirements and creating data retention, documenting procedures for backing up critical data, monitoring backups, and conducting backup restoration testing to ensure recoverability.
#8: Business Continuity
'Business continuity planning (BCP) is the process involved in creating a system of prevention and recovery from potential threats to a company. The plan ensures that personnel and assets are protected and are able to function quickly in the event of a disaster. The BCP is generally conceived in advance and involves input from key stakeholders and personnel.' - Investopedia
Implementation includes having a contingency plan and testing the plan.
#9: Third Party Vendors
Third-party vendors offer innovative, game-changing solutions they offer to the Banking Industry. They play a key role in efficient and profitable functioning. Such dependencies expose banks to third party risks. It also increases exposure to cybersecurity risks and vulnerabilities.
Ensuring that all contracts with them have an SSAE 16, SOC 2 or "right to audit" clause, Defining and monitoring specific service level targets, evaluate controls, risks and financial solvency of the vendor, ensuring that web banking apps are OWASP compliant are the essentials of the IT controls for third-party vendors.
For your bank to be trusted, you must understand the importance of IT controls, and the kind of IT controls needed. We hope this article will help you identify the IT controls needed for your bank or financial institution and put the proper IT controls in place.
For Banking and Financial services Compliance training programs covering a variety of topics, please click here.






