Latin America - Opportunities and Challenges for Pharmaceutical investment and growth, Requirements for marketing Application
The Opportunities
Latin America is a large market with considerable potential for pharmaceutical investment and growth. "The Healthcare landscape in Latin America is changing quickly. Demand is growing as populations age and chronic diseases become commonplace. Increasing wealth in some demographic segments drives a desire for higher quality services. Governments are increasing spending". - Mckinsy report

- It has a total potential patient population of more than 600 million.
- Governments have relatively liberal direct import laws. Doctors can get access to world class medicine.
- The region has well-developed direct sales infrastructure - Import, customs clearance and physical distribution is sophisticated.
- There is high local desire and demand for US and EU products
- Latin America is the fastest-aging region in the world as shown in the following AMI report:

In view of the preceding, foreign pharmaceutical companies want to set foot in these emerging markets. Obtaining marketing authorization (MA) is a key to the entry of foreign companies. Like most other markets, the LATAM markets present challenges too. Understanding the challenges will help in devising the right strategies for MA.
For a detailed understanding of topics ranging from pre-clinical and clinical requirements through product registration, amendments and renewals across Pharmaceuticals, Biologics, Medical Devices and Combination Products, attend the seminar 'Latin America: Regulatory Compliance Requirements for Life Science Products (Focus: Brazil, Mexico, Argentina).'
Key Challenges Companies face in Obtaining Marketing Authorization

Regulatory differences across LATAM
- Although there are sound regional harmonization efforts, regulatory processes to obtain MA are highly country-specific.
- Most countries require considerable information such as raw data from the manufacturing or testing process and more. Obtaining such information can be quite challenging.
- The large amount of time it takes to identify frequently changing requirements in terms of country-specific documentation is a constraint. (Related to infrastructure, legal documents, stability studies, labelling, etc.)
For example consider the following figure from the CIRS R&D 2015 briefing. It outlines the wide array of philosophies, review practice, policies and procedural issues in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Mexico and Peru.
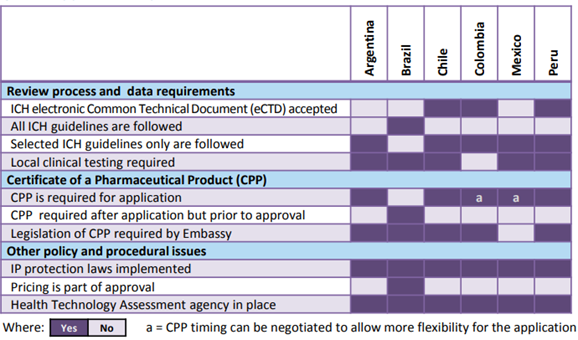
Frequent changes to the local regulations
Frequent changes in regulations, and unclear expectations pose a major challenge to the foreign companies. Tracing the developments and shifts that are particularly significant to the industry is a constraint.
Obtaining Marketing Authorization: Pre-application tasks
In order to optimize the allocation of time and resources, it is essential to identify local MA applications in LATAM in terms of either content or process, and the associated challenges, before the filing of the MA application. Some examples of such are given below:
- The need for a local presence of infrastructure - In many countries, it is required to hold an authorization/certification in order eventually get the marketing authorization as granted by a relevant local authority. In some countries, partnering with a locally authorized company is sufficient. However, foreign companies that partner with the locally authorized partners must make relevant agreements and exercise due diligence before filing the MA application.
- MA application acceptance based on reference agency (EMA/US FDA) - In many cases, the reference from the EMA/US FDA will suffice to serve as a "validation". This again is country specific.
- Quality requirements (chemistry, manufacturing and controls (CMC)) - A significant CMC/Quality section is required as part of the dossiers depending on the country. With regard to stability data, often submit inadequate quantity of data, and incomplete studies. For example, often companies fail to provide data that shows studies under the country's climatic zone conditions, omit the start and end date of the studies, omit data that is needed about relative humidity, and stability under stress conditions for biology/biotech products. Countries have specific formats and guidelines to be followed and duly signed by the person in charge of studies or the manufacturing facility.
Majority of the information required for marketing registration is available at the ICH common technical document (CTD).
The minimum information required for marketing authorization:
Each country has its own application form to request health registrations, in accordance with its own legislation. The minimum information required as per PANDRH, technical document no 10 include:
Administrative and legal information
- Table of contents
- Medicine characteristics
- Legal documentation
- Information on the medicine status in other countries
- Medicines technical information
- Environmental risk assessment
Quality information
- Table of contents with all the documentation
- Contents - Information on information on the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API)
- excipients (E), and finished product (FP)
API
- API. Physicochemical characteristics
- API. Mode of synthesis or process of obtaining for new API
- A flow chart of synthesis process for obtaining the API
- API. Control of the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
E. Excipients
- Name, quality reference, and full description of the quality specifications (indexes and acceptance limits) for each excipient.
- When not from a pharmacopeia, the method of analysis used to verify the quality specifications is required.
- List of animal or human origin excipients and description of the viral safety guarantee and adventitious agents.
- For excipients whose origin implies a risk of transmitting Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE), supporting documents on non-transmission of BSE issued by the appropriate authority are required.
- For excipients used for the first time in a pharmaceutical product or for a new route of administration, the following is required:
Details on its manufacturing process, characterization, and quality control, if applicable. Toxicology information confirming its safety
FP. Finished Product
- FP: Manufacture of the finished product
- FP. Control of the finished product
- FP. Validation of methods of analysis
- FP. Certificates of analysis
- FP. Reference standards and materials
- FP. Description of the container-closure system used
- FP. Stability studies of the finished product
- Post-marketing authorization stability studies programme
- FP. Description of the procedures used to guarantee the cold chain
- FP. Biopharmaceutical documentation
Non Clinical Reports
- Table of contents
- Nonclinical Trials
- The respective pharmacodynamic studies for new combinations
- The respective toxicology studies for new substances added to the formulation, new stabilizers or additives
Clinical Reports
- Table of contents
- Clinical trials
- Clinical trials for known APIs
Attend the seminar 'Latin America: Regulatory Compliance Requirements for Life Science Products (Focus: Brazil, Mexico, Argentina)' to understand the structure of the regulatory agencies in Latin America. The seminar will help you successfully overcome local cultural nuances in working with the regulators.
The course director Robert J. Russell, (Bob) has more than 30 years of experience working with FDA, EMA, Healthcare Authorities and Agencies across Latin America, Middle East and Asia / Pacific supporting clients projects in these regions. Licensing, registrations, GMP, DMFs and borderline products are his core competencies.






