Overview of BSA/AML, OFAC Regulations, and the Regulatory Bodies
Money laundering is rampant globally. 'The estimated amount of money laundered globally in one year is 2 - 5% of global GDP, or $800 billion - $2 trillion in current US dollars.' (UNDOC). The staff of financial institutions, must be aware of their responsibilities in preventing the 'dirty money' entering into the system. They must also understand the Anti-money laundering regulations to ensure compliance as individuals and institutions.
Sadly, some corporates and professionals fail to comply with the regulations due to negligence. Others intentionally violate the regulations. The cost of noncompliance is too high.

Corporate penalties for noncompliance include:
- Loss of Licensing
- Insurance revocation
- Cease and Desist order
- Formal written agreement
- Fines up to $500,000 or 2x the amount involved in the transaction
- Monetary loss from the asset forfeiture actions, fraud, or charge off
- Loss of company value
- Substantial legal fees
- Reputation risks
Personal penalties for violations include:
- Imprisonment up to 20 years
- Personal fines to employees
- Money loss from asset forfeiture action, fraud, or charge off
- Substantial legal fees
- Reputation risk
- Fired or barred from the financial industry
The bottom line: Directors, Management and Staff of financial institutions, Make sure you full understand your regulations and comply!
This article provides an overview of the pertaining BSA/AML and OFAC regulations to help financial professionals comply. It also discusses the regulatory bodies, their functions in brief and directs you to useful resources for compliance.
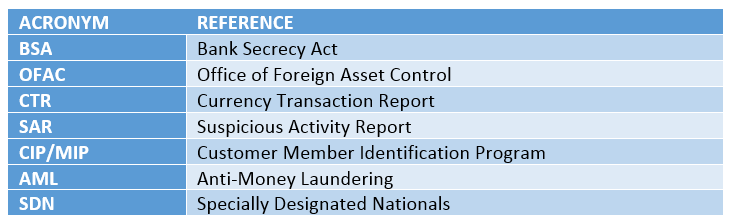
Acronyms used in context
What is money laundering?
Why have the Anti-Money Laundering Regulation?
- Identifying the money laundering risks and fraud
- Protecting consumers from the abuses of financial crime
- Preventing money laundering or the financing of terrorist activities
AML regulatory requirements - What is expected of financial institutions?
- 'Incorporate policies, procedures, and internal controls based upon the loan or finance company's assessment of the money laundering and terrorist financing risks associated with its products and services. Policies, procedures, and internal controls developed and implemented by a loan or finance company under this section shall include provisions for complying with the applicable requirements of subchapter II of chapter 53 of title 31, United States Code and this part, integrating the company's agents and brokers into its anti-money laundering program, and obtaining all relevant customer-related information necessary for an effective anti-money laundering program.'
- 'Designate a compliance officer'
- 'Provide for on-going training of appropriate persons concerning their responsibilities under the program. A loan or finance company may satisfy this requirement with respect to its employees, agents, and brokers by directly training such persons or verifying that such persons have received training by a competent third party with respect to the products and services offered by the loan or finance company.'
- 'Provide for independent testing to monitor and maintain an adequate program, including testing to determine compliance of the company's agents and brokers with their obligations under the program. The scope and frequency of the testing shall be commensurate with the risks posed by the company's products and services. Such testing may be conducted by a third party or by any officer or employee of the loan or finance company, other than the person designated in paragraph (b)(2) of this section.'
Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) - 31 USC 5311
- Lenders are required to file reports of daily transactions conducted in currency in amounts over $10,000.
- Keep records on beneficiaries and originators of funds transfers in amounts over $3,000
- Gather information and keep records on sales of money orders, cashier's checks, and traveler's checks in amounts between $3,000 and $10,000 via escrow or from the company
Key AML Regulators
- Administers and enforces economic sanctions Targeted foreign countries, terrorists and terrorism sponsored organizations, International narcotic traffickers.
- Authority over every financial transactions
- Prohibits business with those on the OFAC lists
- Administers BSA/AML
- Recommends and finalizes rules
- Provides guidance, issue advisories, bulletins and fact sheets
- Gathers and provides information to financial institutions, law enforcement and Insurance companies and others.
- Administers 314 (a) program and 314 (b) voluntary program
- Regulates and supervises all national banks and thrift institutions and the federally licensed branches and agencies of foreign banks in the United States to determine whether or not the bank is operating safely and soundly, providing fair access and treatment to customers, and complying with all applicable laws and regulations.
- The Board of Governors, the Federal Reserve Banks, and the Federal Open Market Committee work together to promote the health of the U.S. economy and the stability of the U.S. financial system.
- Conducts Monetary policy
- Promotes Financial system stability
- Supervises and regulates financial institutions and activities
- Fosters payment and settlement system safety and efficiency
- Promotes consumer protection and community development.
- Primary federal regulator of all federal and state-chartered savings institutions across the nation that belong to the Savings Association Insurance Fund (SAIF).
- OTS issues federal charters for savings and loan associations and savings banks.
- This Bureau also adopts and enforces regulations to ensure that both federal and state-chartered thrift institutions operate in a safe and sound manner.
- Provides deposit insurance to depositors in U.S. commercial banks and savings institutions.
- Examines and supervises certain financial institutions for safety and soundness, performs certain consumer-protection functions, and manages receiverships of failed banks.
- Responsible for enforcing the federal securities laws, proposing securities rules, and regulating the securities industry, the nation's stock and options exchanges, and other activities and organizations, including the electronic securities markets in the United States
- Enforces the Securities Act of 1933, the Trust Indenture Act of 1939, the Investment Company Act of 1940, the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, and other statutes.
- Responsible for collecting taxes and administering the Internal Revenue Code, the main body of federal statutory tax law of the United States.
- Provides tax assistance to taxpayers and pursuing and resolving instances of erroneous or fraudulent tax filings
- Oversees various benefits programs, and enforces portions of the Affordable Care Act.
Useful Resources to help you comply
"Money-laundering is the process that disguises illegal profits without compromising the Criminals who wish to benefit from the proceeds."
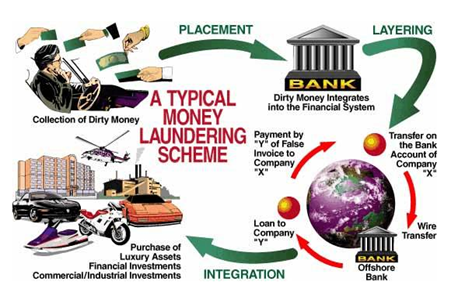
Source: UNODC
Talking about the purpose of the money laundering regulations on 23rd April, 2013, James H. Freis, Jr., the FinCen Director, identified why the AML regulations are needed.
"The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network ("FinCEN") believes that Residential Mortgage Lenders and Originators ("RMLOs" (e.g., independent mortgage loan companies and mortgage brokers) "are primary providers of mortgage finance - in most cases dealing directly with the consumer and are in a unique position to assess and identify money laundering risks and fraud while directly assisting consumers with their financial needs and protecting them from the abuses of financial crime."
The AML helps in:
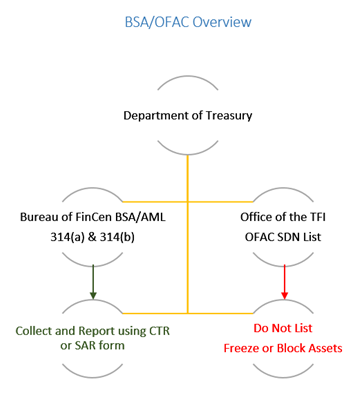
The key regulatory bodies and their functions are discussed in the last section of this article.
Effective August 13, 2012, Lenders (regardless of company size and type of company) must be in compliance and have an AML Program IN FORCE. In accordance with B'1029.210 they should:
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) is the primary U.S. anti-money laundering (AML) law.
The Act is designed to aid federal government in detecting illegal activity through tracking certain cash-based transactions.
BSA requirements:

Compliance officer:
The BSA / AML / OFAC Compliance Officer is responsible for developing, implementing and administering all aspects of the Bank Secrecy Act Compliance Program, and for assuring that the bank is in compliance with the Bank Secrecy Act, USA Patriot Act, OFAC, and all other applicable laws.
Internal controls:
'The board of directors, acting through senior management, is ultimately responsible for ensuring that the bank maintains an effective BSA/AML internal control structure, including suspicious activity monitoring and reporting. The board of directors and management should create a culture of compliance to ensure staff adherence to the bank's BSA/AML policies, procedures, and processes. Internal controls are the bank's policies, procedures, and processes designed to limit and control risks and to achieve compliance with the BSA. The level of sophistication of the internal controls should be commensurate with the size, structure, risks, and complexity of the bank. Large complex banks are more likely to implement departmental internal controls for BSA/AML compliance. Departmental internal controls typically address risks and compliance requirements unique to a particular line of business or department and are part of a comprehensive BSA/AML compliance program .' - Bank Secrecy Act, Anti-Money Laundering Examination Manual
Education and Training:
Well-designed training programs are an integral part of the BSA/AML and OFAC compliance program . While the staff training should be ongoing, it is also important to ensure that it is documented and incorporates the current developments and changes to the BSA/AML regulations. Everyone attending the training must understand their part in maintaining compliance.
Independent Testing:
Testing should include all of the entity's activities and the results to help the Board of Directors and or/Executive management identify gaps, make improvements and establish additional controls. Also, the Company's written policies and procedures, the qualifications of the AML officer, the training materials and attendance logs must be reviewed.
Cyber security:
The Final Rule for Customer Due Diligence (CDD), effective July 11, 2016 for banks and other covered financial institutions to identify and verify the identity of the natural persons behind the legal entity customers - the beneficial owners.
| REGULATORS | FUNCTIONS |
|---|---|
| Office of Foreign Asset Control (OCC) |
|
| Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) |
|
| Office of the Comptroller of Currency (OCC) |
|
| Federal Reserve |
|
| Office of the Thrift Supervision (OTS) |
|
| Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) |
|
| Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) |
|
| Internal Revenue Service (IRS) |
|
BSA Important Issues: new mandates, requirements, and recommendations
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) is a US law that fights money laundering and other financial crimes. BSA requires businesses to keep records and file reports that are determined to have a high degree of usefulness in criminal, tax, and regulatory matters. Individuals and financial institutions who fail to comply with BSA requirements may face severe penalties and for more serious offenses, prison sentences.
How to conduct an effective BSA Audit
BSA rules and regulations must be followed by financial institutions. Although financial institutions have been managing BSA operations in accordance with regulatory requirements, the shift to BSA audits has become increasingly important. Regulators look to the financial institution for confirmation and proof that BSA operations are being audited properly to ensure that BSA efforts are implemented and managed properly.
FFIEC BSA/AML Examination Manual: What Compliance Officers Really Need to Know?
This webinar will go through every section of the revised FFIEC Bank Secrecy Act/Anti-Money Laundering Examination Manual to highlight changes and areas where banks should review their internal policies, processes and procedures for compliance. Understanding these changes will keep you prepared and updated for your next BSA/AML examination.
BSA/AML Crooks, Thieves and Red Flags
This anti-money laundering training will describe the reasons and methods of money laundering in financial institutions. This will help attendees to protect themselves from regulatory risk by establishing an effective anti-money laundering system within their financial institution. Also this webinar will explain various types of money laundering and how to identify the red flags of money laundering in an account within your institution.
Banking MSBs: BSA/AML Risks, Mitigation of Risks and Rewards
In this webinar Banks and Credit Unions (Financial Institutions) will gain a core understanding of the BSA/AML risks, risk mitigation techniques and potential rewards of banking MSBs. This course is designed to assist Financial Institutions in formulating their strategy for banking MSBs, regulatory bodies overseeing MSB compliance, income and expense characteristics in banking MSBs, balance sheet impacts, perceptions and misperceptions of MSBs, risk between MSB entities and how to strengthen your financial institution’s BSA/AML program.
BSA/AML Contextual Awareness of High Risk Customers
This webinar will highlight the steps to identify and evaluate high-risk customers. Learn how to perform BSA, AML risk assessments.
Writing an Effective SAR Narrative
This BSA compliance training on Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR) will provide details on how to prepare a SAR (Suspicious Activity Reporting) narrative that meets examiner scrutiny and provides necessary detail for law enforcement.
Red Flags of Money Laundering
This webinar will explain what money laundering is, various types of money laundering including structuring, micro-structuring and cuckoo smurfing. Attendees will learn how to identify the red flags of money laundering in an account within your institution.
AML/BSA Overview, Compliance, and Current Issues, including new CDD Requirements
This BSA/AML webinar will discuss various compliance requirements for AML - KYC, CTRs, SARs, new customer due-diligence process and various strategies which money launderers are using now and how to detect and thwart it.
AML/BSA Fundamentals, Compliance, and the AML Act of 2020
Money laundering continues to be a national concern. High levels of drug-related activity and violence have drawn additional attention. Terrorist activities need to be considered as well. Perpetrators have adapted to banks’ efforts so banks cannot combat the money laundering with yesterday’s methods.
BSA Training - Tips & Tools
This Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) program training will guide attendees through the methods to train each segment of the bank’s or credit union’s employees annually on Bank Secrecy Act. It can be used as a “Train the Trainer” course or as annual training for all employees.
BSA/AML - What is Old is New Again?
This webinar will provide attendees a clear understanding of the compliance department of the future. Attendees will learn the best practices to ensure BSA and AML compliance and avoid failure and fines.
Monitoring High Risk Transactions
This BSA/AML (Bank Secrecy Act/ Anti Money Laundering) compliance training will help attendees understand, identify and mitigate the risks associated with high risk transactions.
BSA/ AML - Following the Money, the Difference between Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing and How to Combat Both
This AML training will provide you the tools to identify the differences between money laundering and terrorist financing and how to protect your financial institute against potential criminal activity. It will also highlight the complexities of modern day proactive compliance departments.
How to Think Like a Crook - Money Laundering Prevention
This anti-money laundering training will describe the reasons and methods of money laundering in financial institutions. This will help attendees to protect themselves from regulatory risk by establishing an effective anti-money laundering system within their financial institution.
Implementing Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), Audit & Best Practices
This BSA webinar will discuss best practices of development, maintenance and auditing of the Bank Secrecy Act. Common and legal identifiers and red flags, the sources of audit evidence, steps of conducting internal investigation, elements to establish evidence of laundering.
BSA/AML Recent Developments and Compliance
This AML compliance webinar will discuss recent developments in Bank Secrecy Act including various forms such as Currency Transaction Report (CTR), money log and Suspicious Activity Report (SAR).Attendees will learn best practices to ensure compliance with BSA regulations and avoid violations and fines.
What's Hot with BSA/AML and Payments?
This webinar will help attendees to learn the current issues and changes to BSA/AML compliance obligations and the common regulator findings related to payments and customer risk.
Bank Secrecy Act: The Fundamentals - CIP, CDD, EDD, CTR and Fraud Ring Example
This webinar will help understand the fundamental requirements of the BSA/AML statutes and the annual AML training requirements.
Strengthening Compliance with Effective AML Analytics, Algorithms, Machine Learning and Data Science
Learn how effective AML analytics, algorithms, machine learning and data science can strengthen your compliance program. This session will also discuss using analytics to help BSA/AML investigations, how you can use the CDD data gathered along with analytics, model validation and BSA/AML.
AML High-Risk Transactions - Identify, Manage and Resolve
This webinar will discuss the techniques for controlling and managing High Risk Transaction. The Instructor will discuss the parameters for identifying and qualifying transactions as high risk and process and communication to be followed. He will also discuss how to resolve the end result.
Managing an Effective AML Audit Program
This webinar will highlight the techniques and best practices that can be used for conducting an effective AML audit in order to ensure compliance with Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) regulations.
Building an Effective BSA/AML Compliance Program
The prevention of money laundering is a key focus of regulatory authorities in developed countries around the world. Money laundering regulations are designed to inhibit the movement of funds derived from criminal activity and to restrict the availability of money to fund terrorist activities. This training program will detail the historical context of AML regulations, best practices to implement an effective AML program, and reporting guidelines for the same.
Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), Title 31, Compliance
This webinar will review current requirements of the Bank Secrecy Act, why to comply, how to comply, reporting techniques and current positions by the IRS and FinCEN.
Teller Compliance Training: Reg CC, CTR and UCC 3 and 4
This webinar will provide an overview of the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and Regulation CC. It will explain how and when to place holds on deposits. Attendees will understand red flags concerning money laundering and how to complete a currency transaction report (CTR).
Money Service Businesses (MSB): High Risk Account Type
This webinar will highlight the complex efforts in identifying and monitoring of Money Service Businesses (MSB). It will discuss MSB regulatory requirements, documentations, and scenarios that provide guidance on this high risk account type requiring extended due diligence.
BSA Training and Monitoring for Front Line Staff
This bank secrecy act training details how to train your frontline staff and teach them how to monitor for suspicious activity.