Overview of Clinical Data Management and the Regulatory requirements
To gain approval for new drugs, Drug companies must ensure that the clinical data they generate is trustworthy. Clinical data management (CDM) is an important phase in clinical research that leads to the generation of high-quality, reliable, and statistically sound data from clinical trials. Clinical data management includes the entry, verification, validation and quality control of data gathered from clinical trials. A range of computer applications, database systems that support the collection, cleaning and management of clinical data are used in clinical data management.

The concerned personnel in FDA regulated companies must acquire deep knowledge about Clinical data management to use the tools needed to assure a CDM plan that holds up when the inevitable deviations from protocol occur. It is also important to understand how to leverage the vendor and other external resources to apply the best industry practices and avoid potential pitfalls when validating a clinical trial system.
This article provides an overview of CDM, discusses the relevant regulatory requirements and guides you to resources that help you succeed with CDM.
Clinical Data Management - An overview
Data with reference to CDM is the patient information that is collected during a clinical trial.
Clinical data management includes every aspect of processing of clinical data. The outcome of CDM must be a database that is accurate, secure, reliable, and ready for analysis. The timeline involves the time from data entry to analysis.
The objectives of CDM
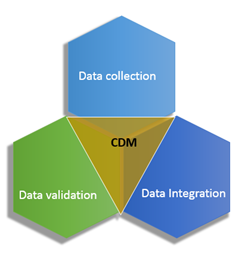
CDM has three main objectives.
- Data Collection - Paper, electronic and remote data capture
- Data Integration - The integration of all data into a single DB to ensure consistence and correctness.
- System/Data validation - This is done via User acceptance testing (UAT), Quality Control (QC) and programming through edit check programs and manual review.
CDM activities include:
- Data management plan
- Study set up
- Training
- Data collection
- Data processing
- Monitoring of data and its safety
- Audit trail
- Database (DB) closure
- Security and confidentiality
- Data archive
Data management plan:
The data management plan (DMP) is a living document throughout the life-cycle of the study addressing the updates or changes performed during the course of the study. It should be created for each study should start early during the setup of the study. It should specify
- What work is to be performed?
- Who is responsible for the work?
- What guidelines and SOPs should be complied with?
- What is the expected output of the product?
All responsible staff should review and reach a consensus with the DMP to ensure consistency of the process.
Study setup:
It must include:

Trial DB setup:
All data should must be entered and setup in the computer system within a structured DB.
Validation checks:
It must include
- Checks for missing values
- Range checks
- Logically inconsistent checks
- Protocol violation checks
- Checks for duplicates
Training:
Training must be consistent across all materials and be delivered consistently.
Data collection:
It includes Clinical data capture at study sites via paper CRFs and EDC systems. The primary modes of data capture are
- Offline
- Online
- Combination of offline and online methods
Data processing:
It must include
- Data receipt - Data receipt may be received through fax, regular mail, express mail, private couriers, hand delivery, web entries.
- CRFs tracking - Both mandatory and optional CRFs must be tracked
- Data review - CRFs must be reviewed manually and query sheets should be reviewed for data errors.
- Data coding - Methods include manual and automated coding
- Data entry:
- Single-pass entry: with manual review and without manual review
- Double pass entry has two types
- Blind verification involves two people entering data independently. In records where discrepancies are found between the two, a third person resolves the record based on the verification records that failed data entry verification
- Double entry with interactive verification: Two people enter data and the 2nd DE operator resolves discrepancies between 1st and 2nd entry while being aware of the previous values
- Optical character recognition (OCR)
- Data validation - must be performed at the time of data entry and should also be run on batches of data. They include pre-defined validation rules to detect like missing details, outliers, inconsistencies, protocol etc.
- Query management
Monitoring data
- Progress reports
- Interim analysis
- Site monitoring visits
- Training and re-training staff
- Auditing
- Adverse Event Reporting
- Data Safety Monitoring Board
Audit Trails:
An audit trail (also called audit log) is a security-relevant chronological record, set of records, and/or destination and source of records that provide documentary evidence of the sequence of activities that have affected at any time a specific operation, procedure, or event. (IA glossary).
Audit trials may include documents, computer files, and other records that are examined during an audit to demonstrate how the records are handled by a company. Computer generated time-stamped audit trails are used to give credence and providence to electronic records and signatures.
Database closure:
Before closure it must be ensured that all data have been processed, Quality level has been evaluated and appropriate study personnel has been notified. After closure, edit permissions must be removed.
Database storage:
Must be secure, efficient and must have controlled access. Measures should be taken to minimize data corruption via accidental or intentional manipulation
Data archive:
Original study documents, raw data files, Final data files, Discrepancy management logs, Database design specifications, DB closure documentation, and Procedural variation documentation should be archived in secure and stable areas.
---------
Closed systems: Closed systems are those systems where a company can verify the identity of all users prior to granting access to electronic records and electronic signatures (ERES) system.
Open systems: Open systems are those systems where a company cannot verify the identity of all users prior to granting access to an ERES system. Digital signatures are needed in addition to electronic signatures.
Procedural requirements: The indenting to use ERES must inform the FDA about it. The company must verify the record and the identity before granting signature access to a user. The user should be trained not to share their e-signature with anyone else.
--------
Understanding the regulations
In the mid-1990s, when companies increased adaption of computerized electronic keeping, they were met with a whirlwind of challenges in maintaining the integrity and robustness of electronic records. To streamline the management of electronic records, the CFR Part 11 regulations were created in 1997.
- 21 is the chapter of US Federal law - Food, Drug & Cosmetics Act circa 1906
- CFR is the code of regulation - US Federal Government law
- Part 11 is that part which deals with electronic records and electronic signatures.
Part 11 applies to all FDA regulated industries including all Drug and Medical Device Manufacturers that sell into the United States and use electronic records and electronic signatures. The U.S. Federal Regulation requires companies to ensure that the electronic records they deal with are trustworthy.
The Part 11 covers:

Electronic Recordkeeping:
Any quality or production record held in electronic format. These include batch records, training records, customer complaint records and more. Just as quality and production paper records are legal documents that can be submitted for legal proceedings, electronic records too can be used as equivalents. Just as tampering or altering a paper record is considered as fraud, the tampering or altering of electronic records is equivalent to forging a paper record and is considered as fraud.
Electronic Signatures:
Any approval of a quality or production record that is committed electronically. The electronic signature comprises of two parts.
- Publically known identifier, typically a user name to identify the user uniquely and trace their job role and training record to verify their level of authority and competence
- Known only to the owner of the eSignature typically a password or biometric data to ensure that it the right person is signing
Electronic Submissions:
NDAs, 510(k)s, PMAs etc.






