Pharmaceutical CMO Selection and Qualification Audits - Getting it right
Outsourcing has become a key business strategy. Over the years, the healthcare industry has shown significant progress in capitalizing on it. Contract manufacturing organization (CMO) assist healthcare companies to manage their comprehensive operations on a contract basis including drug development, formulation development, stability studies, drug manufacturing and more. Healthcare companies are rapidly outsourcing their manufacturing activities in order to reduce manufacturing costs while maintaining quality.

Although outsourcing presents many advantages, there are major constraints too. Supply chain complications and issues related to control of third party pose a considerable threat to the healthcare contract manufacturing. How can Companies ensure that they get the first step which is the CMO selection and qualification audit right?
This article provides answers to this question focusing on the healthcare industry segment 'pharmaceutical contract manufacturing.'
Before diving into the control of third-party organizations, it is important to know the regulations pertaining to the contract manufacturing in order to ensure compliance right from the selection and qualification auditing to the entire lifecycle of the supply chain management.

The regulatory requirements
Contract Manufacturing Arrangements for Drugs: Quality Agreements Guidance for Industry
- "Owners are responsible for approving or rejecting drugs manufactured by the contract facility, including for final release. In all cases, the owner must not introduce or deliver into interstate commerce, or cause to be introduced or delivered into interstate commerce, any drugs that are adulterated or misbranded."
Controls should be exercised
- For both owners and contract facilities that conduct manufacturing operations, CGMP "includes the implementation of oversight and controls over the manufacture of drugs to ensure quality, including managing the risk of and establishing the safety of raw materials, materials used in the manufacturing of drugs, and finished drug products."
A comprehensive quality system model should be used
- "Owners can use a comprehensive quality systems model to help ensure compliance with CGMP...Quality agreements should clearly describe the materials or services to be provided, quality specifications, and communication mechanisms between the owner and contract facility."
ICH guidance for industry
- Q7 Good Manufacturing Practice Guidance for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients recommendations for owners
- "Evaluate contract facilities to ensure that contractor sites comply with CGMP for specific operations
- Have approved written agreements with contractors that define the manufacturing responsibilities in detail, including the quality measures, of each party.
- The written agreements should also define considerations for subcontracting; describe how changes to processes, equipment, methods, and specifications will be managed; and permit the owner to audit its contractor's facilities for compliance with CGMP."
- FDA Safety & Innovation Act (FDASIA- 2012) :
- "FDASIA includes a set of provisions, contained in Title VII of the statute, which give FDA new authorities to address the challenges posed by an increasingly global drug supply chain."
- Eudralex, Vol. 4, Ch.7- Outsourced Activities
- "The pharmaceutical quality system of the Contract Giver should include the control and review of any outsourced activities. The Contract Giver is ultimately responsible to ensure processes are in place to assure the control of outsourced activities."
- Eudralex, Vol. 4, Ch. 5- Production
- "The holder of the manufacturing authorisation shall verify such compliance either by himself or through an entity acting on his behalf under a contract."
CMO selection, qualification and audits
The next step after understanding the regulations is the selection of CMOs. CMO selection is a critical step to the success of your product. Hiring a wrong CMO is one of the most costly mistakes a pharmaceutical manufacturer can make. The following section explains 9 effective steps to CMO selection.
1. Assess product needs
Establishing a 'Clarity of the requirements' is the first step to needs assessment. What you actually require from the contract manufacturing organization determines the cost and efficient use of your time and in-house resources. Put your requirements in writing and then evaluate each CMO's level of satisfaction for each requirement.
2. Assess Company's needs and risk tolerance level
Performing an assessment for the kind of partnership your company is wishing to seek with the CMO is crucial to vendor selection. This includes an evaluation of the people they want to work with and the working relationship they would like to have. Even if the CMO is capable, if the values, culture, and work ethics don't match up with each other, the partnership won't work well. It is also important to evaluate your risk tolerance level for financial losses and delays that may occur during the contract. Once you are clear about your risk tolerance levels, establish guidelines and bottom lines for what kind of risks are acceptable and what is non-negotiable.
3. Develop criteria for CMO selection
Developing a criteria table with a score based system will simplify your CMO selection process. You can fill in the scores in the next phase and total them. Here's an example
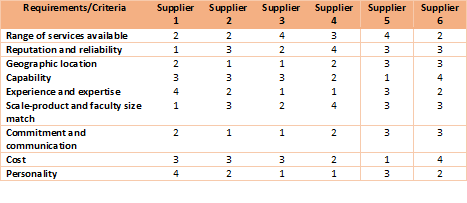
4. Create a list of Potential CMO candidates and start engaging potential CMOs
Develop an information matrix as shown in the example below. This will help you track communication between you and each candidate.
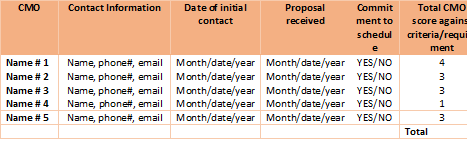
5. Shortlist potential CMOs
Remove the CMOs that don't qualify your top requirements from the list and retain top suppliers. Reorganize them in your priority based on your qualification thus far.
6. Onsite visit
Visiting the CMO facility will help you understand how the CMO operates. This is your opportunity to get a firsthand view of the cleanliness and functions of the facility and get to know the most relevant departments including Engineering, Quality, Scales and Corporate, and the Project Management team. If the on-site visit convinces you of the CMO's capabilities and matches with your requirement, set up an audit and request for proposal (RFP).
7. Audit and proposal
Spend adequate time at each CMO site. Direct visits will help you with first-hand information for the criteria scoring and information matrix tables (tables 1 and 2). The audit will assist you in determining whether to do business with them. If they meet your criteria, you can proceed with reviewing the CMOs documentation and continue the project discussion. Let them know that you expect them to submit a proposal in response to the audit.
8. Negotiate the contract
It is best to negotiate the contract with at least 2 CMOs as there are chances of the partnership drop-offs before the signing of the contract. You can bid adieu to potential CMOs only after you have signed a mutual agreement with one. Keep the lines of communication open until signing off the final contract.
9. The partnership begins
Now starts the new partnership journey. Beyond qualification, auditing and selection of CMOs, there is a lot involved in effective oversight of Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Organizations.
Attend the seminar 'Effective Quality Oversight of Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs)' to understand how to manage CMOs- from start to finish. The seminar will shed in-depth light on Selection and Qualification, Quality Agreements, Understanding of CMO Operations, and Review of Key CMO Records. This practical how-to course is designed to provide participants with skills they can immediately apply to CMO oversight within their own organizations.
The speaker Andrew Campbell has 25 years of pharmaceutical quality assurance and quality systems experience in both industry and consulting roles. Mr. Campbell has worked in clinical supply and commercial manufacturing environments and has experience with integrated manufacturing and contract manufacturing business models. He has extensive expertise in the areas of deviation - CAPA, change control, GMP auditing, GMP training, and regulatory inspection preparation and management.






