The Importance of Pharmaceutical Validation for Long-Term Success
- Acceptance specifications should be set up to achieve the desired product attributes consistently and uniformly
- Specifications should be obtained from testing and challenging the system on a sound statistical foundation during the early development and production phases, and continuing through subsequent routine production
The pharmaceutical industry employs high-end materials, complex facilities and equipment, and highly skilled workers. The optimal utilization of these resources is critical to the industry's long-term performance. Product failures, rejects, reworks, recalls, and complaints account for a considerable portion of total production costs. If failure is to be controlled and productivity improved, a detailed study and control of the production processes are required

What do you think? Is validation really important - not only for optimal use of resources but also for your company's sustainable success?
Some companies are reluctant to make sufficient investments in validation. Due to the pressure to cut costs, there is a tendency to cut corners. However, they do not realize that it can lead to an increased compliance risk.
With clear project objectives and methodologies, and engagement of all stakeholders consistently, proactive risk management, trained validation team, and good communication, the project objectives can be realized within budget and project deadlines.
Validation optimizes the following costs

Validation optimizes processes:
Optimizing facility, equipment system, closures, etc. helps produce a product that meets quality standards while being less expensive. People who are well-trained and competent are critical components of process optimization, which leads to increased efficiency and production.
Validation helps achieve and maintain the quality goal:
Companies that take on validation projects seriously are likely to achieve and maintain the quality goal, and no wonder. GMPs are built around validation and process control. It is hard to achieve quality products without a validated and controlled process. As a result, validation is an important part of ensuring product quality.
Validation enhances safety:
Equipment and gauges that are properly calibrated and certified are used to decrease accidents and increase safety. Thus, validation increases operation safety.
Validation enhances customer care:
Market recalls can be prevented with adequate validation, resulting in greater customer service and product quality.
Validation is a regulatory requirement:
Validation standards must be met in order to gain approval to produce and introduce new items.
What you can do
Develop a master validation plan
Every step of the validation process should be planned. A validation master plan (VMP) or related documents should clearly describe and document the key aspects of a validation program. It should be brief and unambiguous. It may be essential to construct different validation master plans for large projects.
Elements of a validation master plan
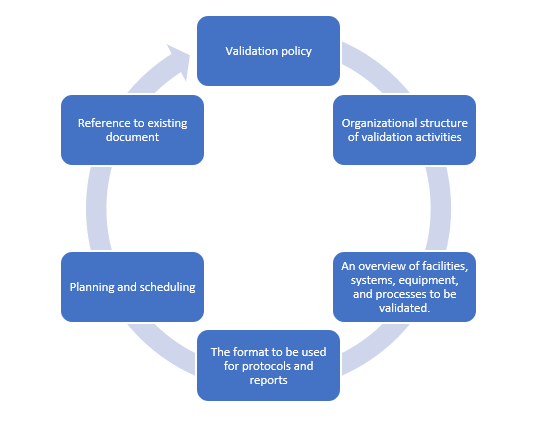
Document how validation and qualification will be conducted
Create a written protocol specifying how the validation and qualification will be conducted. The written protocol should be duly reviewed and approved. Critical steps and acceptance criteria should be specified in the protocol. A format release for the next step in qualification and validation should be made as a written authorization after the completion of a satisfactory qualification.
A report should be created that summarizes the results collected, comments on any deviations seen, and draws the required conclusions, including recommending adjustments to remedy deficiencies, and that cross-references the qualifying and/or validation protocol. Any deviations from the protocol's design should be documented and justified.
Set up the validation
Validation must be set up to establish the desired physical and chemical attributes. For parenterals, the desired attributes must include stability, the absence of pyrogens, and the absence of visible particles.
The method and equipment to be validated should be chosen to meet the product requirements. Each phase of the process should be tested to verify its suitability, and the method should be outlined with great precision. These factors are critical in ensuring consistent product quality, purity, and performance.
Pharmaceutical Validation Training
The various regulatory agencies have expectations that pharmaceutical manufacturers will demonstrate control over their manufacturing equipment. The FDA's findings of deficiencies concerning equipment validation indicate the agencies expect definitive evidence that the equipment qualification and validation schedules of a facility will satisfactorily control their manufacturing processes. Examples of FDA form 483 findings for equipment qualification and validation indicate deficiencies in many of these studies.
To learn more about equipment qualification, and process validation, attend the virtual seminar Global Regulations for Equipment Qualification and Validation of Processes in the Pharma Manufacturing.






