Reducing Regulatory Burdens with MDSAP
For medical device manufacturers, gaining access to multiple major markets is important for the success of the company. However, to enter multiple markets, they have to comply with the guidelines, regulations, procedures and deadlines of various regulatory jurisdictions that govern the markets they want to operate. During this process, Companies are subject to multiple audits by many agencies that have their own processes, jurisdictional requirements, and scientific principles. These rigorous audits require time and labor of many personnel within a company during the inspection and follow up actions.
A globally consistent approach to the auditing and monitoring of medical devices minimizes the regulatory burdens and eliminates redundancy and enhances safety and efficacy. That's where the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP) comes in.

The History of Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP)
Initiation: With view that a global approach to auditing and monitoring the manufacturing of medical devices could improve their safety on an international scale, the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) established a work group in 2012. The objective was to establish a single, global audit program known as MDSAP as a substitute for Regulatory Authority (RA) inspections.
Pilot program: A pilot program was initiated in January 2014 with a number of international regulatory partners.
The pilot program was replaced by the full-program launch on January 1st, 2017.
MDSAP today as an Active Program
"The Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP) is a program that allows the conduct of a single regulatory audit of a medical device manufacturer's quality management system that satisfies the requirements of multiple regulatory jurisdictions. Audits are conducted by Auditing Organizations authorized by the participating Regulatory Authorities to audit under MDSAP requirements."
Currently, MDSAP includes the regulatory jurisdictions and agencies of:
- United States: Food & Drug Administration or FDA (Quality System Regulation 21 CFR Part 820)
- Canada: Health Canada or HC
- Brazil: AgC*ncia Nacional de VigilC"ncia SanitC!ria or ANVISA (RDC ANVISA 16/2013)
- Australia: Therapeutic Goods Administration or TGA (TG(MD)R Sch3)
- Japan: Ministry of Health, Labo ur and Welfare, and the Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency or MHLW/PMDA (MHLW Ministerial Ordinance No. 169)
The World Health Organization (WHO) Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics (IVDs) Programs and the European Union (EU) acted as official observers of the project. Others Regulatory Authorities may eventually decide to participate in the MDSAP and to become active participants in the Program.
MDSAP Guidance and Documents
- FAQ
- MDSAP Audit Models (ISO 13485:2016)
- MDSAP Companion Documents (ISO 13485:2016)
- MDSAP Policies, Procedures, Templates and Forms
- Nonconformity Grading System for Regulatory Purposes and Information Exchange
- MDSAP members' regulations
MDSAP Eligibility
Medical Device Manufactures who wish to participate in the MDSAP can be located anywhere globally. However their medical product must fall under the scope of at least one participating regulatory authority and be compliant with their quality management system requirements.
4 ways to internally prepare for MDSAP certification
- Conduct a gap assessment of all SOPs and processes with an eye toward risk
- Develop and implement a comprehensive risk assessment program
- Ensure Employees are fully competent in ISO 13485:2016
- Perform a preliminary preparatory audit by experienced third party consultants
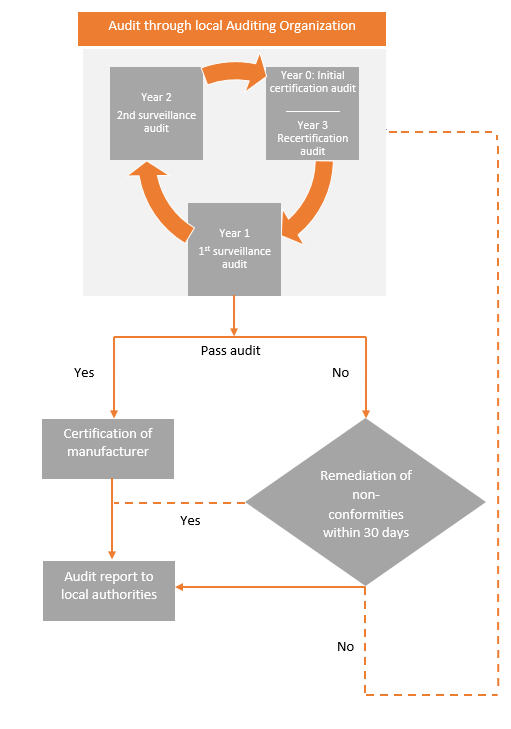
3 year Audit Cycle
- The Medical Device Single Audit Program is based on a three year audit cycle.
- The Initial Audit, also referred to as the "Initial Certification Audit" is a complete audit of a medical device manufacturer's quality management system (QMS) consisting of a Stage 1 Audit and a Stage 2 Audit.
- Partial Surveillance Audit :The initial Audit is followed by a partial Surveillance Audit in each of the following two years
- A complete Re-audit, also referred to as a "Recertification Audit" in the third year.
- Special Audits: Audits Conducted by Regulatory Authorities, and Unannounced Audits are potential extraordinary audits that may occur at any time within the audit cycle.
List of Auditing Organizations
Auditing Process
MDSAP Eligibility
MDSAP has replaced the traditional grading criteria such as significant finding, "regular finding" and "significant opportunity for improvement" with a point based grading system.
First, a 4-point grading matrix is used to assign points to non-conformities written against requirements in ISO 13485:2016. Second, the initial point score is applied to a series of escalation rules that may or may not result in a higher final point grade.
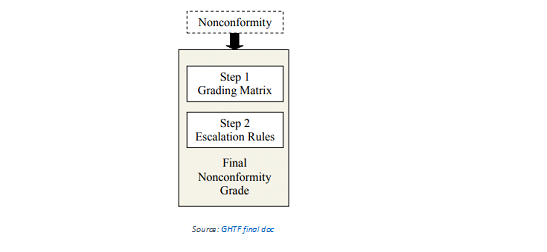
The grade determined by the first step is increased by 1 point for each rule that applies in the
Absence of a documented process or procedure
Or
Release of a Nonconforming Medical Device
The final nonconformity is graded between 1 and 6, a grade of 5 or more is determined to carry a high enough risk that intervention is required.
Business Benefits of participating in MDSAP
- Access to multiple markets via a single audit
- Expected future expansion to more countries
- Tandem ISO certification
- No routine FDA inspections (unless for a "for cause" or directed inspection)
- Saves your Business money and minimizes administrative overheads
- Saves significant amount of your time thus helping you to enter markets faster
- Reduced regulatory burden
- Fewer audits resulting in less business disruption
- Less audit preparation
- Reduced staff expenses
- Increased focus on delivering safe, effective and technologically advanced products
- No Publically available reports (public reporting or FOIA)
Recommendations for MDSAP Participation
- Become well acquainted with the language in the regulation
- Clearly understand the exact requirements
- Become well acquainted with what is not specified
- Be able to pinpoint where the regulation/directive stops and perhaps personal interpretation begins
- Always take the ethical, high-road in your discussions
- Be courteous, respectful in all your interactions
- Be prepared to take issues to higher officials if you feel you have a strong case and you are not being heard
- Develop a network of contacts across agencies
- If at joint meetings, trade shows, get to know the people personally, if appropriate
- When in doubt about something Call for clarification
- Work to build long-term trust
Attend the Seminar Medical Device Single Audit Program [MDSAP] Implementation & Participating Country Regulatory Processes: U.S., Canada, Brazil, Australia and Japan to understand how MDSAP certification is a valuable pursuit to your organization and the steps involved.






