Understanding HIPAA Compliance, its latest modifications, and guidance
If your organization is subject to HIPAA compliance audit, it is important to familiarize yourself with the regulations to ensure adherence. Noncompliance can result in heavy fines, criminal charges and civil action lawsuits should an electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) breach occur. Whether the violation is deliberate or inadvertent, the Office for Civil Rights of the Department of Health and Human Services (OCR) will not consider your defense justifiable. This article is designed to help your organization stay HIPAA Compliant.

What is HIPAA compliance?
- It means adhering to the requirements of The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996, its amendments, and related legislation such as the HITECH Act. The last major update of the rule was in 2013.
- HIPAA's intention is to reform the healthcare industry by reducing costs, simplifying administrative processes and burdens, and improving the privacy and security of patient information.
- The HIPAA defines requirements for the privacy and security of Protected Health Information (PHI).
What problems does it solve?
- Prior to HIPAA, changing jobs meant changing insurers and resuming waiting periods. This was extremely frustrating. The HIPAA eliminates this portability issue by preventing insurance lapses, enabling easier exchange of information, and facilitating better coordination of benefits.
- Using the electronic system to process large numbers of claims quickly presents new challenges. Information is valuable, it should be protected. The HIPAA regulations help solve the new information handling problems.
How can organizations solve the new problems of using electronic systems for information handling?
With automation, information is easily accessible or transported. By taking the right steps to prevent information breaches, organizations can solve the new problems of using electronic systems for information handling.
- Establish policies and procedures in-line with the HIPAA regulations to help your staff practice compliance
- Impart initial and ongoing training to staff
- Motivate support and cooperation of the entire staff
Who is covered under the HIPAA?
- Covered Entities: Covered entities are Healthcare providers, health insurance providers, and employer-sponsored group health plans that deal directly with protected health information.
- Hybrid Entities: Employers that provide self-insured health cover or benefits such as Employee Assistance Program (EAP). B' 164.103 Definitions
- Workforce Members: The covered entity is responsible for the actions of its workforce - Employees, Contracted Staff, Volunteers, Agents.
- Business Associates: An individual or business that provides a service or performs a certain function or activity for a covered entity that involves the business associate to access to PHI maintained by the covered entity. Examples include medical billing companies, medical storage, marketing organizations, software companies, medical device manufacturers, etc.
HIPAA Rules
The 4 major rules to understand on the path to HIPAA Compliance are below:

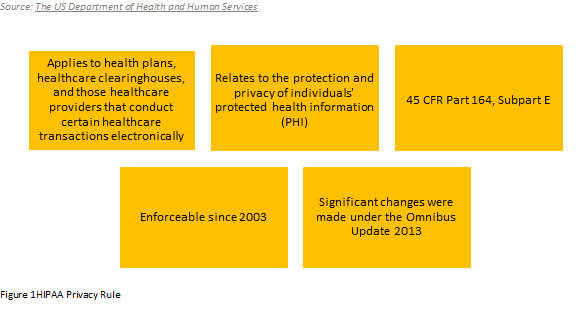
HIPAA Privacy Rule
"The Rule requires appropriate safeguards to protect the privacy of personal health information, and sets limits and conditions on the uses and disclosures that may be made of such information without patient authorization. The Rule also gives patients' rights over their health information, including rights to examine and obtain a copy of their health records and to request corrections."
HIPAA Security Rule
"The HIPAA Security Rule establishes national standards to protect individuals' electronic personal health information that is created, received, used, or maintained by a covered entity. The Security Rule requires appropriate administrative, physical and technical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and security of electronic Protected Health Information."

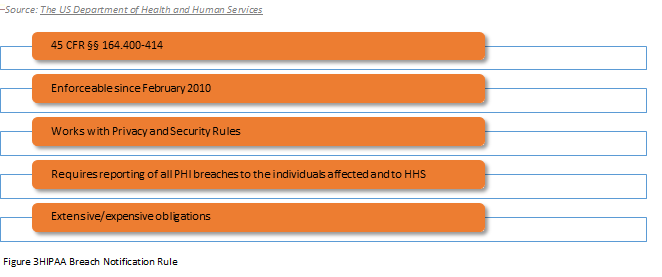
HIPAA Breach Notification Rule
"A breach is, generally an impermissible use or disclosure under the Privacy Rule that compromises the security or privacy of the Protected Health Information."
HIPAA Enforcement Rule
"The HIPAA Enforcement Rule, 45 CFR Part 160, Subparts C-E, establishes rules governing the compliance responsibilities of covered entities with respect to the enforcement process, including the rules governing investigations by the Department, rules governing the process and grounds for establishing the amount of a civil money penalty where a violation of a HIPAA Rule has been found, and rules governing the procedures for hearings and appeals where the covered entity challenges a violation determination."

Best Practices for conducting Internal Audit of your compliance before facing the HIPPA Audit:
- Ensure that your organization's Policies and Notice of Privacy Practices are in line with the HIPAA rules
- Review processes for handling patient rights
- If there were issues identified in Breaches identified in the prior audit, ensure they don't repeat.
- Complete the HIPAA Audit Protocol
- Prioritize issues identified and plan their mitigation
- Verify that Policies and Procedures are being followed
- Document all your HIPAA Compliance Activities
- Review your own compliance instead of letting others find the gaps.
Resources to help you answer questions you might face during the audit
- HIPAA audit: The 42 questions HHS might ask
- Sample - Interview and Document Request for HIPAA Security Onsite Investigations and Compliance Reviews
- Questions asked of a small provider after a data breach involving theft of a laptop and server
- Questions asked in the first round of 2012 HIPAA random audits
- Audit protocol - updated 2018
Professionals who may be interviewed include CEO/President/Director, HIPAA Officer, Systems Director, Security Officer, Network Engineers, Network Administrators, Hardware specialists, DR/backup specialist, Physical Access manager, HR, Training Director, Incident Response leader and others as they may request.
Attend the Seminar HIPAA Privacy Rule Compliance-Understanding New Rules and Responsibilities of Privacy Officer to understand audits and enforcement in detail, and how privacy regulations relate to security and breach regulations, as well as responding to privacy and security breaches and ways to prevent them.
The speaker Jim Sheldon-Dean has more than 30 years of experience in policy analysis and implementation, business process analysis, information systems and software development. He serves on the HIMSS Information Systems Security Workgroup, has co-chaired the Workgroup for Electronic Data Interchange Privacy and Security Workgroup, and is a recipient of the WEDI 2011 Award of Merit.






