- By: Staff Editor
- Date: September 06, 2017
Access Regulatory Compliance Training sessions led by expert panelists below.
Compliance Webinars |
Virtual Seminars for Professionals
ICH Q3D Elemental Impurity Guidelines: Are You Prepared for January 2018?
While both ICH Q3D and USP General Chapters <232> and <233> are scheduled to go into effect in 2018, implementation requires extensive prior work. The new elemental impurities limits require more sophisticated analytical technology, such as ICP-MS, not routinely used in QC labs. The ultra-sensitive analytical method must be validated specifically for all of your different dosage forms.
What are Elemental Impurities?
Elemental impurities are traces of metals that can be present in finished drug products. These impurities may arise from several sources, such as residual catalysts that were intentionally added in product's synthesis or from contact with manufacturing equipment, containers and other materials. Since these impurities do not contribute to any therapeutic benefit to the patient, and in certain cases might harm the patient, it is important to measure and control their levels within the acceptable limits.
Elemental Impurities Classification
ICH Q3D guideline classifies 24 elements into three classes based on their toxicity (permitted daily exposure, PDE) and likelihood of occurrence in the drug product.
Class 1: Class 1 elemental impurities are significantly toxic and may come in the final drug product from commonly used materials (e.g., mined excipients). These elements require consideration during risk assessment across all routes of administration. Elements in this class are As, Cd, Hg, and Pb.
Class 2: Elements in this class are further divided in sub-classes 2A and 2B based on their likelihood of occurrence in the final product.
- Class 2A are relatively likely to appear in final drug products due to their natural abundance, thus require risk assessment across all routes of administration. The elemental impurities in this class are Co, Ni and V.
- Class 2B are less likely to be incorporated into final drug products due to their low abundance, thus require assessment only if they are intentionally added. Ag, Au, Ir, Os, Pd, Pt, Rh, Ru, Se and Tl are included in this class.
Class 3: The elemental impurities in this class are relatively nontoxic via the oral administration route but require consideration in the risk assessment for parenteral and inhalational routes. Ba, Cr, Cu, Li, Mo, Sb, and Sn.
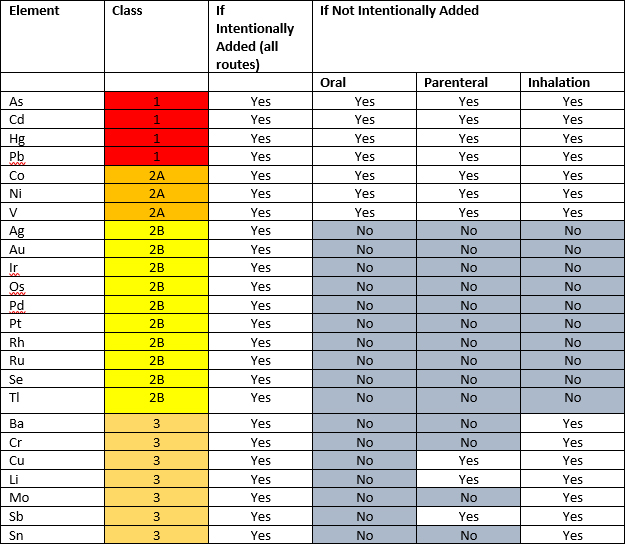
Table 1: Summary of the elements included in each class where risk assessment is required
Guidance Requirements and Implementation Timelines
The ICH finalized the Q3D guideline for elemental impurities in December 2014 and recommended for its adoption in ICH regions: USA, Europe and Japan.
In line with this, the US FDA, in June 2016, has published the draft guidance on elemental impurities in drugs to help manufacturers comply with ICH and USP standards.
The requirements of the US FDA guidance apply to:
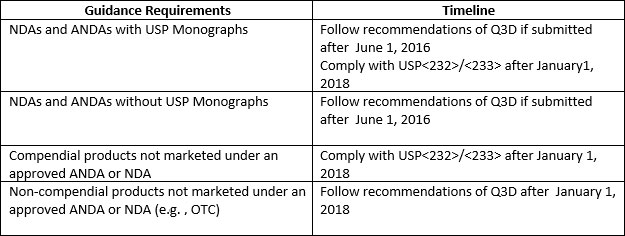
Table2: Guidance Requirements and Implementation Timelines
Similarly EMA has set the implementation dates for ICH Q3D guidelines:
- New drug products submitted for approval in Europe must comply with the ICH Q3D guidelines by June 2016.
- Existing products must comply by December 2017
Guidance Applicability
The guideline applies to new finished drug products and new drug products containing existing drug substances.
However it doesn’t cover:
- herbal products
- radiopharmaceuticals
- vaccines
- cell metabolites
- DNA products
- allergenic extracts
- cells, whole blood, cellular blood components or blood derivatives including plasma and plasma derivatives
- dialysate solutions not intended for systemic circulation
- products based on genes, cells and tissues
- drug products used during clinical research stages of development.
The implementation of ICH Q3D is a significant milestone to harmonize control of elemental impurities worldwide. Practical implementation of ICH Q3D establishes a risk based approach. The fundamental challenge, however, is to find a means to categorize risk. This means an exhaustive assessment of all the components of manufacturing including API, excipients, water, manufacturing equipment, processing aids, and container closure system to determine their contributions to all elemental impurities.




















